At MyFundedFutures, we see the same story play out again and again: traders spend weeks hunting for the “perfect strategy,” but fail the evaluation because they never built a plan for how to execute it.
A futures trading plan isn’t just about chart patterns or indicators. It’s about bridging strategy with consistent action — under the real constraints of prop firm rules, account sizes, and trailing drawdowns.
The most effective plans share three traits: simplicity, repeatability, and reviewability. Let’s break down how to design a plan that not only works in theory, but also keeps you consistently profitable and if it’s your goal — get funded.
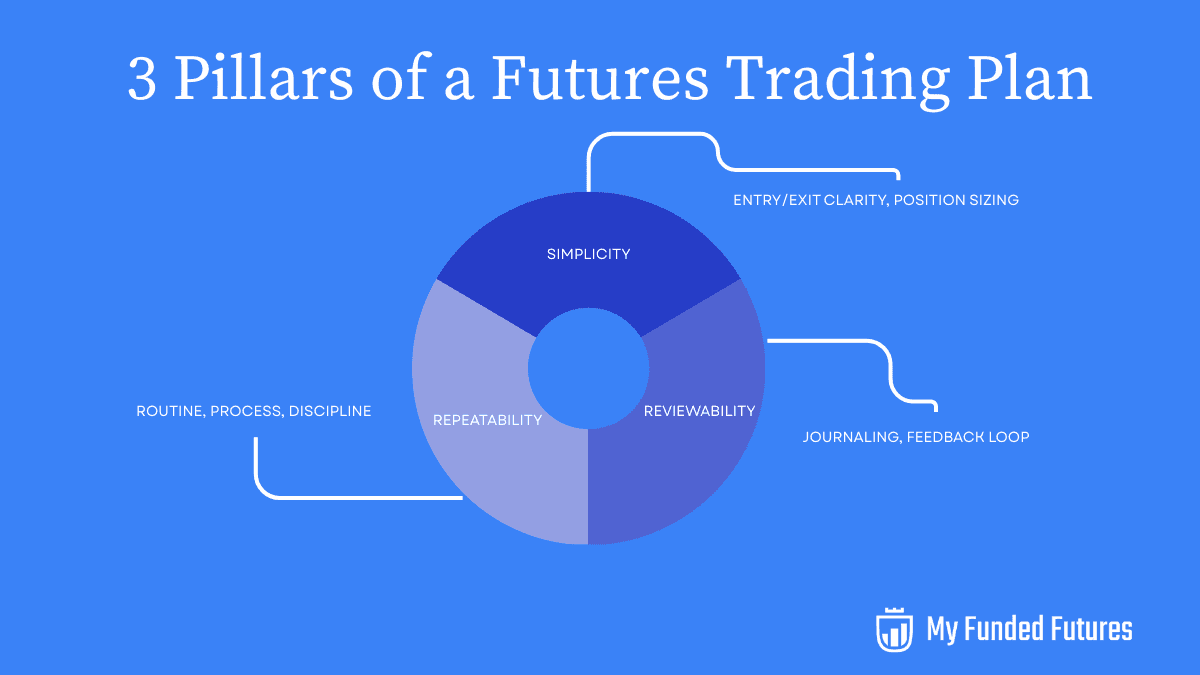
Keep Things Simple
Overcomplicated strategies often lead to analysis paralysis and costly mistakes, when faced with high-pressure situations in the market. By contrast, embracing simplicity allows traders to react swiftly, even when the market whipsaws.
Focus on defining trading rules for yourself that are easy to follow.
-
Entry rules: Define specific conditions that must be met before you enter a trade. Example: “Enter long in the E-mini Nasdaq when price clears yesterday’s high with volume confirmation, only during U.S. morning session.”
-
Exit rules: Decide in advance where you’ll cut losses and where you’ll take profits. Prop firms don’t tolerate holding and hoping — a trailing drawdown can wipe you out fast if you move stops.
-
Position sizing: Standardize risk. Many traders cap exposure at 1% of account equity per trade, adjusting contracts to fit stop distance. If your $50K evaluation allows two micros max, build your plan around that reality.

- Markets and sessions: Narrow focus. If your edge is in equity index futures during New York hours, don’t wander into crude oil during Asia.
If you can’t summarize your plan on one page, it’s too complicated.
Build for Repeatability
Futures trading rewards consistency; it is what separates trading from gambling. A string of disciplined trades is more valuable than one oversized home run.
A well-designed trading plan establishes standardized processes that generate consistent results across different days and market conditions.
Repeatability makes results measurable.
-
Pre-market routine: Follow a standardized pre-market preparation routine each day. Check the economic calendar, overnight price action, and key levels before Globex opens.
-
Execution: Enter and exit the same way every time. If your plan says two conditions must align, don’t improvise or deviate on the fly.
-
Risk rules: Stick to the same max loss per trade and per day. If your plan says “three losses, stop trading,” that’s it. Don’t give in to excitement or frustration.
Consistency is what lets you track stats, refine setups, and — most importantly — survive long enough to get funded.
The Feedback Loop
Without structured reviews, no trader can objectively identify what works, what fails, and why certain patterns recur in their performance.
Every trade should feed back into your growth.
- Journal everything: Record entry, exit, contracts, reasoning, and mindset. Include screenshots. Do it on paper or digitally, as it suits you.
- Review regularly: Weekly reviews reveal patterns. Maybe your Nasdaq setups crush trends but bleed in chop; that’s actionable insight.
- Refine deliberately: Don’t overhaul your plan after a bad day. Adjust only when your data shows a recurring weakness.
A good trading plan treats mistakes as tuition, but only if you study the lessons.
Look at your winners and losers and ask: Did I follow my plan? Was the setup truly there or did I deviate due to emotion? How was the market environment, and did my strategy handle it well?
Over a series of trades, you will start to see what themes emerge.
Know When Not to Trade
One of the fastest ways traders blow accounts is by trading when they shouldn’t. Knowing when to stay out of the market is just as important as knowing when to get in.
- Market conditions: Thin holiday sessions or high-volatility news events (like Fed announcements) can create random moves that break your edge. Unless your plan is built for it, stay flat.
- Personal readiness: If you’re tired, stressed, or distracted, sit out. A single bad decision can trigger the daily loss limit and end your session.
- Risk environment: If volatility spikes far beyond normal (ATR or VIX extremes), reduce size or avoid trading until conditions normalize.
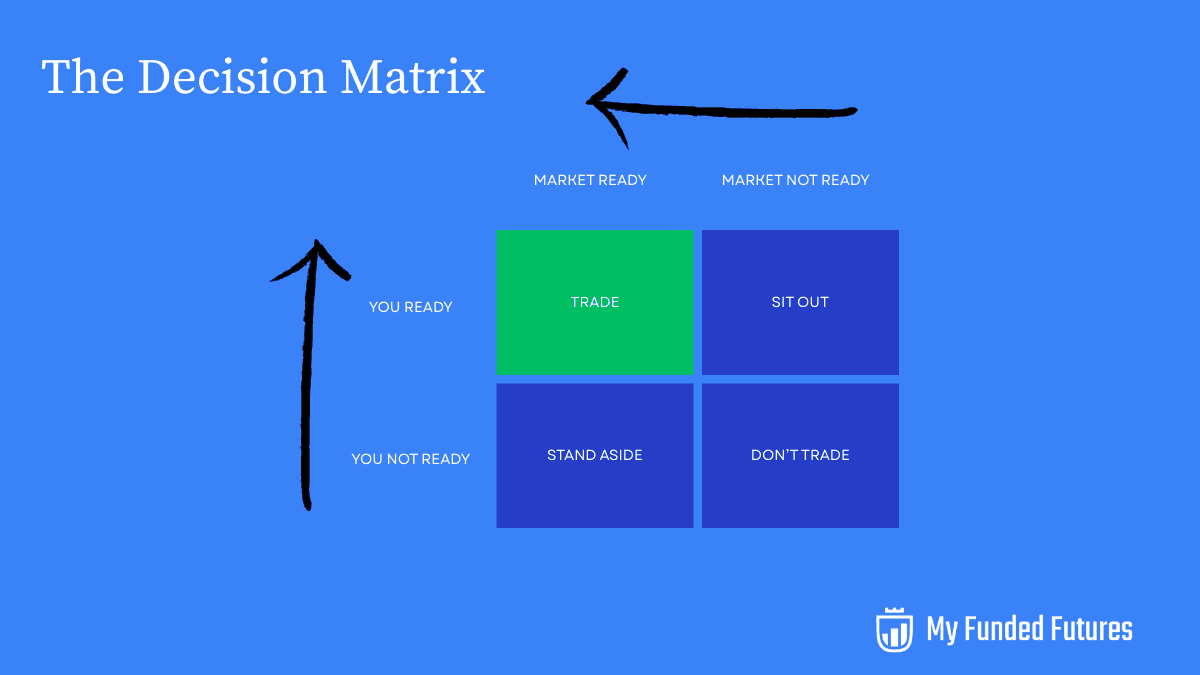
Capital preservation is survival. In prop firm trading, not trading is sometimes the best move you’ll make.
Structure Creates Freedom
Rules may feel restrictive, but structure actually creates freedom by removing uncertainty.
-
Daily caps protect you: A rule of max 3 losses per day stops revenge trading before it costs you the account.
-
Checklists reduce mistakes: Pre-market prep (levels, news, platform setup) and trade-entry checklists prevent slip-ups.
-
Less mental load: With decisions pre-defined, you can focus on execution, not improvisation. Structure keeps you calm and clear when it counts.
Forming Your Futures Trading Plan
A successful futures trading plan is comprehensive – covering everything from how you analyze the market to how you manage risk and keep records. But it is also small and easy to follow.
Market Analysis Framework
- Define how you will identify trading opportunities. Professional traders combine technical analysis with any relevant fundamental or sentiment factors.
- Show precision when you set up your plan. Example: “Trade E-mini S&P pullbacks to the 20-EMA during trending days. Avoid entries within 30 minutes of CPI or FOMC releases.”
- Specify which contracts you’ll trade (micros vs minis) and why.
- Make conditions concrete: instead of “buy dips,” write “buy first pullback to the 20-EMA after a 20-day high, provided retracement is <50%.”
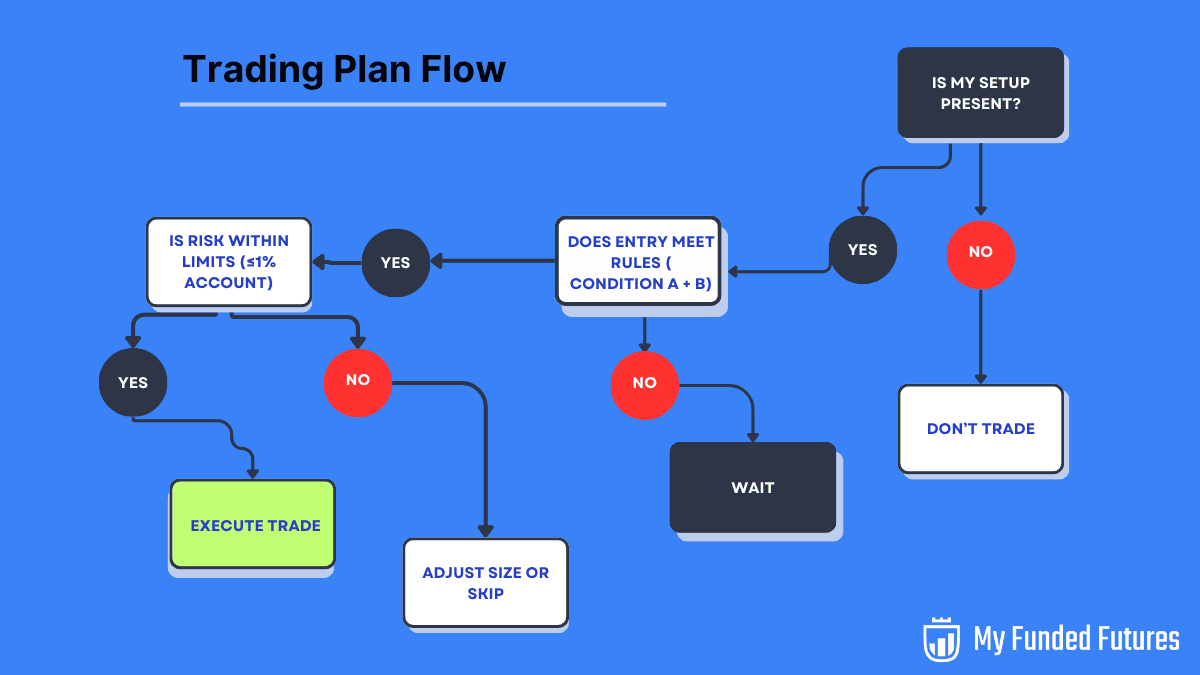
Risk Management
Position sizing: the formula or rule for how much volume you trade (contracts or lots) based on your account size and the trade setup.
Stops: Predetermine where your stop will go for each strategy. Whether it's a technical level or a fixed amount, write it down. And crucially, honor your stops: no moving them once a trade is live, unless your plan allows for a trailing stop method.
Daily/weekly loss caps: set a daily loss cap, like at 3% of the account; align this with the prop firm's rules if you are funded. If hit, they stop trading for that day to limit the damage and reset mentally. Include this in your plan to avoid spiraling on a bad day.
Exposure: Limit correlated trades. Two positions in ES and NQ can double your risk exposure.
Reward-to-risk: Target at least 2:1 setups so wins cover inevitable losses.
Record-Keeping & Review
- Log every trade, including screenshots and reasoning.
- Categorize setups so you see which pass firm rules and deliver profits.
- Review weekly, focusing on rule adherence as much as P&L. A lucky win outside the plan is a red flag, not a success.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Over-Optimization and Complexity: This happens when traders try to create a "perfect" strategy by adding more and more rules and filters, often to eliminate past losing trades. The result is usually a convoluted plan that looks great on historical data but falls apart in live trading. Over-optimization means you've excessively fine-tuned your strategy to fit the past perfectly, to the point it's too specific to those past conditions.
The telltale sign is a strategy that performs amazingly in backtest but then underperforms moving forward. Embrace the fact that no strategy can avoid all losses.
Practically, if you find your plan has so many rules that you have trouble remembering or executing them, that's a red flag.
Skipping testing: Deploying a new idea live without sim trading it first means bursting your account.
In the excitement of a new idea, beginner traders skip simulated testing or jump in with full size too soon. The danger is discovering issues only after you've lost real money.
For example, maybe the strategy had an unseen bias or you didn't account for commission costs, or it's very hard to execute in fast markets.
Avoid drastically changing your strategy parameters without testing the impact. Sometimes even a small tweak like a different stop method can change the performance profile significantly.
If you do tweak something, monitor your results closely to make sure you end up benefiting from the change.
Discipline lapses: Most traders don't fail because of strategy. They fail because they break rules after a loss or two. Anchor yourself with accountability
Share your plan or results with a trading buddy or mentor who can call you out if you stray. Or write down your rules and place them in plain sight as you trade.
Similarly, set process-oriented goals -- "I will follow my plan 100% this week" rather than P&L goals, for example. This keeps you focused on what you can control, i.e. your actions.
Having predefined responses for emotional situations helps. If you hit your daily loss limit, your plan says "stop trading and review what went wrong." Doing so means you have an action to follow, rather than feeling lost.
Final Thoughts
At MyFundedFutures, we emphasize this: passing an evaluation isn't about predicting markets better than anyone else. It's about showing discipline, protecting capital, and proving you can operate like a professional.
A strong futures trading plan:
-
Keeps rules simple enough to follow under stress.
-
Repeats consistently so results can be measured.
-
Includes reviews that refine your edge.
-
Defines not only when to trade, but when to step aside.
Structure gives you freedom. With a plan that fits both your strategy and prop firm constraints, you give yourself the best chance to get funded --- and stay funded.
This material is provided for educational purposes only and should not be relied upon as trading, investment, tax, or legal advice. All participation in MyFundedFutures (MFFU) programs is conducted in a simulated environment only; no actual futures trading takes place. Performance in simulated accounts is not indicative of future results, and there is no guarantee of profits or success. Fewer than 1% of participants progress to a live-capital stage with an affiliated proprietary trading firm. Participation is at all times subject to the Simulated Trader Agreement and program rules.
Frequently Asked Questions
Rate this article
Related Posts
Read our most popular posts
Which Prop Firms Offer Daily Payouts and How Do They Work?
Daily payout prop firms let traders withdraw profits far more frequently than traditional models, sometimes even from the very first funded day. Instead of waiting weeks for a payout cycle, traders can request withdrawals every day, subject to rules on drawdown, buffers, and minimum amounts. This guide explains how daily payout structures work, which futures prop firms are known for fast withdrawals, what to watch out for in the fine print, and how MyFundedFutures’ Rapid plan fits into this newer payout landscape.
What Is MyFundedFutures Scale Account and Is It The Right Plan For You?
The MyFundedFutures Scale Account is a middle-tier evaluation plan that balances affordability with growth potential. The scale plan offers weekly payout opportunities with increasing withdrawal limits, no daily loss cap, and a clear path to live funding after just five consecutive payouts.
5 Best Prop Firms With NinjaTrader Integration
NinjaTrader's advanced charting and precision execution tools make it a top choice for active futures traders, but not every prop firm integrates it smoothly. We'll highlight five firms that support true NinjaTrader compatibility, how their setups compare, and which one gives you the most stable, consistent path from evaluation to funded account.


